This is due to the unusual nature of the proline side chain which forms a covalent bond with its own mainchain nitrogen generating a closed ring. The union of two amino acids results in a dipeptide which possesses a free amino group N-terminus.

Nutrition Proteins Openlearn Open University
The used tRNA is released back into the cytosol so it can bind to another amino acid.
. Place by Hydrogen bonds between the H of Nδ-Hδ group and the O of CδOδ-of the fourth amino acid along the chain N CH C R O N CH C R O H N CH C R O N CH C R O H δ-δ-δ δ δ δ-δ-. In this kind of condensation two amino acids approach each other with the non-side chain C1 carboxylic acid moiety of one coming near the non-side chain N2 amino moiety of the otherOne loses a hydrogen and oxygen from its carboxyl group COOH and the other loses a. For exampleAdding more amino acids producesoligopeptides and finallypolypeptides Fig.
Ø The resulting compound after the peptide bond formation is called a dipeptide. R-CHNH 2COOHEach amino acid is a monomer that forms a peptide polymer chain with other amino acids when the carboxyl group -COOH of one amino acid reacts with the amino group -NH 2 of another amino acid forming a. Isoleucine is one of only two common amino acids with two chiral centers.
Special proteins will detach the string of amino acids from the last tRNA and the protein will be released. The peptide bond is unique in its properties. The word Peptos is in turn derived from the word péssin which means to digest.
AAPPTec offers high purity histidine derivatives for solid phase and solution phase peptide synthesis. A polypeptide is a longer continuous unbranched peptide chain. Among the numerous metabolic effects of GLP-1 are the glucose-dependent stimulation of insulin secretion decrease of gastric emptying inhibition of food intake increase of natriuresis and diuresis and modulation of rodent β-cell proliferation.
They are short strings ie between two and fifty. Ø One molecule of water is eliminated during the formation of peptide bond by the condensation reaction of two amino acids. Ø A dipeptide has a free amino group at one end and a carboxylic group at.
This dipeptide can also form additional peptide bonds because of the presence of free amino group and carboxylic group at its N-terminal and C-terminal respectively. Peptides are smaller versions of proteins. Peptides from Ancient Greek πεπτός peptós digested from πέσσειν péssein to digest are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
In the presence of 150 mM NaCl the activity of. Although it is a single. 3 When a peptide is comprised of two amino acids it.
Characteristics of Peptide Bonds. The resulting bondbetween the carbonyl group carbon atom and the amine nitrogen atom is called a peptide link or peptide bond. The peptide is taken from the Greek word Peptos which means digested.
Peptide bonds are strong with partial double bond character. The glucagon-like peptide-1 GLP-1 is a multifaceted hormone with broad pharmacological potential. Eventually the mRNA will present a codon to the ribosome that means stop.
Adipeptide is formed by a reaction between the α-carboxyl and α-amino groups of two amino acids. The amino acids in polypeptides are held together by peptide bonds. Cis peptide bonds are only common when the amino acid proline lies on the C-terminal side of the bond.
During the reactions that occur the resulting CO-NH bond is the peptide bond and the resulting molecule is an amide. Singular amino acids are the building blocks of life and can be linked to form oligopeptides polypeptides and proteins inside the cellThis occurs during a process called protein synthesisVarying sequences of the. Insulin may be shown by clicking the appropriate button in the blue-shaded rows.
A peptide is a compound consisting of amino acids connected by a peptide bond particularly between the carboxyl group of one amino acid the amine group of another amino acid. When two amino acids form a dipeptide through a peptide bond it is a type of condensation reaction. The ribosome acts as a large catalyst forming peptide bonds between amino acids.
Their job is to bring the mail electrons to. The polypeptide definition describes a chain of more than twenty and less than fifty amino acids bound together via covalent peptide bonds. Ø Peptide bond formation is an example for a condensation or elimination reaction.
In Boc chemistry HisBom should be utilized when histidine racemization is critical. The resultant compound is called a dipeptide. Designed an ideal α-helical peptide with a length of 11 amino acids and inserted Cys at the N-terminal C-terminal and appropriate central position of the peptide to form disulfide bonds respectively Fig.
A peptide is a molecule consisting of two or more amino acids linked together by peptide bondsThe general structure of an amino acid is. The four-atom functional group -CONH- is called an amide group or a peptide group. Since each of the original amino.
Polymeric is another form of multivalent AMPs to investigate the salt resistance of homo-dimer AMPs Nan et al. Think of NADH and FADH2 as mail couriers. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides and include dipeptides tripeptides and tetrapeptides.
Helical conformations of peptide chains may also be described by a two number term n m where n is the number of amino acid units per turn and m is the. 25Each peptide has anamino terminus conventionally written on the left side and acarboxyl terminus written on. Seven hydrogen bonds that together provide roughly 30 kcalmol stability help to maintain this conformation.
Isoleucine is hydrophobic and promotes the formation of β-sheets. It has the characteristics of a partial dual bond. During this process a water molecule is removed which creates a peptide bond between two amino acids.
The formation of the bond results in the production of a molecule of water in general reactions that result in the production of water when two other molecules combine are referred to as condensation reactions. The amino acids are linked by peptide links which are the. The end result is loads of energy approximately 34 ATP energy molecule.
Each polypeptide chain is a series of amino acids joined together in a specific sequence.

When Two Amino Acids Condense To Form A Dipeptide What Is The Other Product Of The Reaction Enter Brainly Com
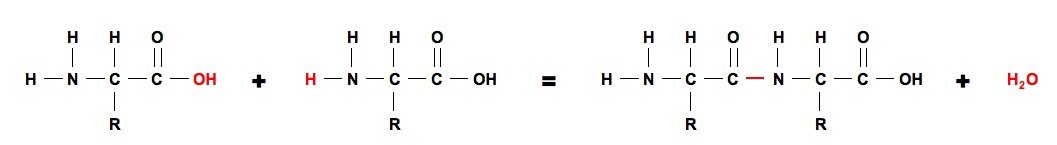

0 Comments